Scalability, Fidelity, and Containment in the Potemkin Virtual Honeyfarm
Background
Major Attacks: buffer overflow attack, and other attacks such as: SQL injection/Attack (enter SQL statement which could be executed in the name field);
Network HoneyPot(蜜罐):
HoneyPot 是一种诱惑hacker 攻击的服务器,黑客误以为honeypot 里面有自己想要的数据。世界第一个少年黑客曾经攻击,SanDiego Supercomputer center honeyPot, 结果被捕。
HoneyPot 分为两种
low-interaction:只是模拟port, 不运行任何程序,容易扩展到很大规模
high-interaction:运行程序,成本高,每一个IP address ,都需要一个physical host.
HoneyMonkey:
Emulate human-being to enter malicious website
Issue/Motivation:
Increase scale of honeypot, while remain high fidelity
CPU,memory 利用效率低,通常只有1%利用率; most address don't receive traffic most of the time; most traffic that is received causes not interesting behavior; Don't have much modification
Balance high scalability(only emulate simple network) and high performance (full physical machine)
Challenge:
-Honeypot detection: malware can detect it is a honeypot
-Resource exhaustion: under high load, difficult to maintain accurate illusion.
Solution:
-Virtual Machine: easy to manage like: frozen state(snapshot), migrate, stored on demand. Copy-on-Write memory sharing
-aggressive memory sharing
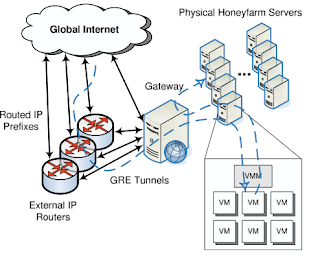
-Containment: Allow no traffic out to contaminate other machine in the network
-late binding of resource
只有有需求的时候才会create new Virtual machine, router 把信息分配到 honeyfarm server,server 再create VM
Major Attacks: buffer overflow attack, and other attacks such as: SQL injection/Attack (enter SQL statement which could be executed in the name field);
Network HoneyPot(蜜罐):
HoneyPot 是一种诱惑hacker 攻击的服务器,黑客误以为honeypot 里面有自己想要的数据。世界第一个少年黑客曾经攻击,SanDiego Supercomputer center honeyPot, 结果被捕。
HoneyPot 分为两种
low-interaction:只是模拟port, 不运行任何程序,容易扩展到很大规模
high-interaction:运行程序,成本高,每一个IP address ,都需要一个physical host.
HoneyMonkey:
Emulate human-being to enter malicious website
Issue/Motivation:
Increase scale of honeypot, while remain high fidelity
CPU,memory 利用效率低,通常只有1%利用率; most address don't receive traffic most of the time; most traffic that is received causes not interesting behavior; Don't have much modification
Balance high scalability(only emulate simple network) and high performance (full physical machine)
Challenge:
-Honeypot detection: malware can detect it is a honeypot
-Resource exhaustion: under high load, difficult to maintain accurate illusion.
Solution:
-Virtual Machine: easy to manage like: frozen state(snapshot), migrate, stored on demand. Copy-on-Write memory sharing
-aggressive memory sharing
-Containment: Allow no traffic out to contaminate other machine in the network
-late binding of resource
只有有需求的时候才会create new Virtual machine, router 把信息分配到 honeyfarm server,server 再create VM
评论